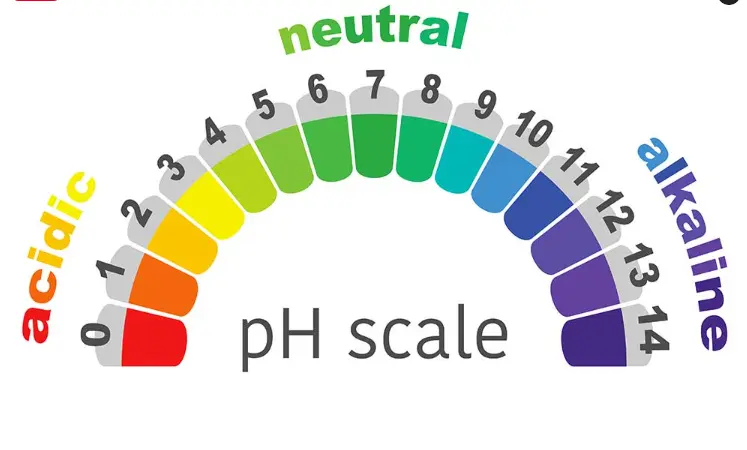
Meaning of pH of water
The full form of pH is potential of hydrogen.
pH of Water
- The pH of water is the logarithm of reciprocal of hydrogen ion activity in moles per liter.
- The value of pH starts from 7 mainly due to hydrolysis of salts of strong bases and weak acids or vice versa.
- The pH value of water is also affected by presence of carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulphide and ammonia in the water.
- The industrial waste may by strongly acidic or basic pH value depends on receiving water depends on the buffer capacity of water.
- The pH value under testing in the laboratory may not be same during the time of collection due to reaction with sediments, hydrolysis, and absorption of gases and reduction / oxidation takes place in the sampling bottle.
|
Water |
pH Value |
|
Natural water |
6 to 8 |
|
Alkaline thermal springs waters |
> 9 |
|
Acidic thermal springs waters |
4 or even less than 6 |
Courtesy: Havells
For more details: Read this article
How pH of water is determined?
- The pH value may be determined either electrometrically or calorimetrically.
- The electrometric method is more accurate but it requires some special apparatus.
- The calorimetric method is simple and requires less expensive apparatus. It is accurate for general work. It is subject to interference with high saline content, colour, turbidity, free chlorine and various reluctant and oxidants.
You may also like to read these articles also
What is meaning of DPSU in Defence?
pH Scale
|
pH Value |
|
|
0 |
Acid, Battery |
|
1 |
Stomach Acid |
|
2 |
Lemon |
|
3 |
Vinegar |
|
4 |
Tomato |
|
5 |
Coffee |
|
6 |
Milk |
|
7 |
Water |
|
8 |
Blood |
|
9 |
Baking Soda |
|
10 |
Stomach Tablets |
|
11 |
Ammonia Solution |
|
12 |
Soap |
|
13 |
Bleach |
|
14 |
Drain Cleaner, Alkaline |